| Advertisement |
Classification of Foundation
On the basis of depth, foundations are broadly classified into two categories.
- Shallow foundation
- Deep foundation

Shallow foundation :
"The foundation is known as the shallow foundation that immediately beneath the lowest part of the structure, near to the ground level."
OR
“A shallow foundation is a type of building foundation that transfers building loads to the earth very near to the surface, rather than to a subsurface layer or a range of depths as does a deep foundation.”
Such foundations are mostly placed below ground level on the first hard strata. Shallow foundations are those that at shallow depth transmit the loads to the soil.
When the soil at shallow depth is strong enough to withstand the load, a shallow foundation is provided The ratio of foundation depth D to foundation width, B is equal to or less than 1 for shallow foundations.
For shallow foundation:
D / B < 1
Deep foundation :
The foundation built sufficiently below ground level is called the deep foundation at its base with some artificial arrangements such as piles, wells, etc.
Deep foundations are those transiting the load into deeper soil. Deep foundations are required when a structure can not be supported by the soil at shallow depth and a hard stratum is available at larger depth.
For deep foundations, the ratio of the depth of the foundation to the width of the foundation is greater than 1.
D / B > 1
Types of shallow foundation:
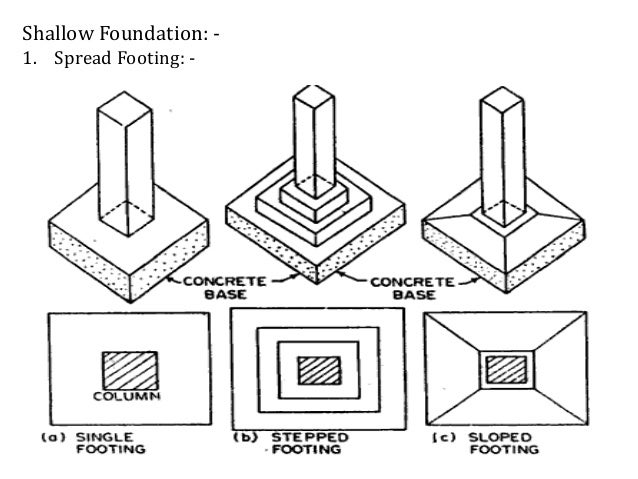
- Spread footing or open trench foundation.
- Raft or Mate foundation.
- Stepped footing.
- Inverted arch footing.
Spread footing or open trench foundation:
The spread foundation is the shallow foundation type. It is defined as the structural components used to support the column and wall as well as to transmit and distribute the load on the structure to the soil.
In plan, the shape can be circular, square and rectangular.
In such foundation, the spread is given under the base of a wall or a column by providing offsets. This spread is known as footing and the foundation itself is called spread footing.
Wall footing, Masonry pillar footing, and Concrete column footings. ( isolated and combined) are the types of spread footing.
Wall footing:
This is a typical and simplest form of spread footing. It consists of the number of brick courses, the lowest being usually twice the above wall thickness.
By having 50 mm offsets on either side of the wall, the base width of the wall is increased.
Each course usually has a depth of 100 mm.
The course at the bottom is 200 mm deep.
The size of offsets is slightly more in the case of stone walls.
Used for ordinary building walls.

Masonry wall footing:
The isolated footing is used to support the individual pillars and columns constructed in brick or stone masonry.
Concrete column footing:
These are either stepped type, type of slate or type of slope with projections in the concrete base. Reinforcement is also provided at the base to support heavy loads.
Raft or Mate foundation:
The foundation that consists of a thick R.C.C slab that covers the entire area in the form of a mat is known as a raft or mat foundation.
The entire area is excavated to the specified depth in the construction of the Raft Foundation.
The bed is compacted and water-sprinkled.
A layer of lime concrete or lean concrete (1:8:16) is then laid to an appropriate thickness to act as a base cover.
The reinforcement is laid after that. The reinforcement consists of closely spaced bars placed between them at right angles.
Then the cement concrete (1:2:4) is laid and compacted to the thickness required.
This type of foundation is useful for public buildings, office buildings, school buildings, residential quarters, etc, where the ground conditions are very poor and bearing power of the soil is so low that individual spread footing cannot be provided.

STEPPED FOUNDATION :
Another type of foundation is stepped foundation, For Stepped Foundation Construction, excavation is performed in steps with the short length and uniform thickness and the masonry work is performed on the horizontal concrete bed thus prepared.
If the structure can be slipped body-wise, R.C.C piles can be driven on the sloping side along with its base concrete.

Strap footing :
A strap footing is a component of a building's foundation. It is a type of combined footing, consisting of two or more column footings connected by a concrete beam.
This is the most common type of foundation used where you have a solid soil base and a logged area of nan-water.
With this type of foundation, most small buildings of just one floor are constructed.
Depending on the recommendations of the structural engineer, the size of your foundation for the small building could be 600 mm to 1200 mm.
Types of deep foundation:
- pile foundation
- well foundation
Pile foundation :
A pile is basically a long cylinder of a strong material like concrete that is pushed into the ground to act as permanent support for structures built on top of it.
The foundations of the pile are deep foundations. These are composed of long, slender, columnar structures that are usually made of steel or reinforced concrete, or sometimes wood. When its depth is more than three times its width, a foundation is described as' piled.
Pile foundations are used when the surface has a layer of weak soil. This surface can not bear the building's weight, therefore the building's loads must bypass this layer and be moved to the layer of stronger soil or rock below the weak layer.
it is also when there are heavy concentrated loads in a house, such as a high-rise tower, bridge, or water tank.
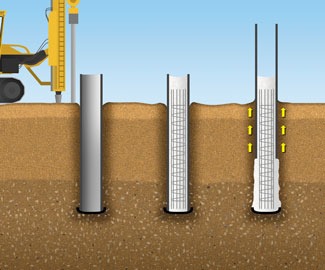
Types of Pile Foundation
01. Based on Material:
Timber pile
Steel pile
Concrete pile
Composite pile
02. Based on Shape:
Cylindrical pile
Tapered pile
Under-reamed pile
03. Based on Load Transfer Mode:
End bearing pile
Friction pile
04. Based on Construction Method:
Cast-in-site reinforced concrete
Precast reinforced concrete
05. Based on the Installation Method:
Bored pile
Driven pile
Vibrated pile
Well foundation:
Well foundation is a type of deep foundation that is usually provided for bridges below the water level. Cassions or well have been in use since the Roman and Mughal periods for bridge foundations and other structures.







0 comments: