| Advertisement |
What Is Leveling?
Leveling is a civil engineering survey branch of measuring levels at different points with respect to a fixed point such as building elevation one-point height from the surface, etc.
Stadia Leveling:
Types of Leveling in Surveying.
- Direct leveling
- Trigonometric leveling
- Barometric leveling
- Stadia leveling
Direct Leveling:
It is the most commonly used leveling process. Measurements are directly observed from the leveling instrument in this process.
Direct leveling is divided into different forms on the basis of observation points and instrument positions as follows:
- Simple
leveling
- Differential
leveling
- Fly
leveling
- Profile
leveling
- Precise
leveling
- Reciprocal leveling
Simple leveling:
It is a simple and fundamental method of leveling in which the instrument of leveling is positioned between the points to be found in elevation. At that point, leveling rods are placed and viewed by means of a leveling instrument. Only when the points are nearer to each other without any barriers is it done.
Differential leveling:
When the distance between two points is greater, differential leveling is performed. The number of interstations is located in this process and the instrument is shifted to each station and the elevation of interstation points is observed. Finally, the difference is determined between the initial two points.
Fly leveling:
When the benchmark is very far from the workstation, fly leveling is performed. In such a case at the work station, a temporary benchmark is placed based on the original benchmark. It is used to evaluate approximate standard, even if it is not highly accurate.Profile leveling:
Typically, profile leveling is adopted to identify points along a line such as a road, rail or river, etc. In this case, intermediate station readings are taken and each station's reduced level is found. From this alignment, the cross-section is drawn.
Precise leveling:
Precise leveling is similar to differential leveling, but higher precision is expected in this case. Serious analysis technique is conducted to achieve high precision. The accuracy is achieved by 1 mm per 1 km.
Reciprocal leveling:
If the leveling device can not be found between the inter-visible points, reciprocal leveling is carried out. In the case of lakes or streams, etc., in the case of mutual leveling, the instrument is placed closer to the first station and sighted to the second station.
Trigonometric Leveling:
It is called trigonometric leveling the leveling process in which the point elevation or the difference between points is determined from the observed horizontal distances and vertical angles in the field. Trigonometric relationships are used in this method to calculate a point elevation from an angle and horizontal range, so it is called trigonometric leveling. It is also referred to as indirect leveling.
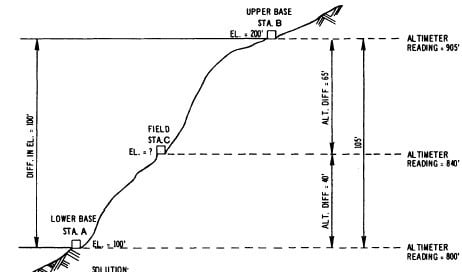
Barometric Leveling:
A barometer is an instrument used to calculate at any altitude atmosphere. Thus, in this leveling method, atmospheric pressure is observed at two different points on the basis of which the vertical difference is determined between two points. It is a rough estimate and is rarely used.
Stadia Leveling:
It is a modified form of trigonometric leveling in which the principle of Tacheometer is used to calculate the point elevation. The line of sight is angled from the horizontal in this case. It is more accurate and suitable in hilly terrain for surveying.














zabrdast sir.
ReplyDeletegood
ReplyDelete